By: Kathryn Gerardino-Elagio
As the technology becomes more intelligent, controllable and varied, automation and robotics are expected to play a bigger role in producing and creating value. When it comes to the trend of using automation and robotics, Thailand is no exception. The Thai government has implemented numerous measures to promote the growth of these key industries. The use of industrial robots in the country is thus anticipated to continue rising.
Speaking to more than 150 participants at a recent virtual conference on “ASEAN Smart Factory Summit 2022: Automotive Manufacturing Industry,” organised by Ringier Events, Mr. Chanin Khaochan Thailand Board of Investment (BOI)’s Deputy Secretary General talked about Thailand’s Smart Factory Investment Promotion Policy.
Mr. Chanin explained that that the government recognises the importance of automation and robotics and has paid attention to both demand and supply sides in designing effective investment incentives so as to create the right financial ecosystem in the country. Such incentive packages are offered for both existing and new investment projects.
Supply side
On the supply side BOI’s investment support measures are offered to a wide range of business activities related to robot and automation, which includes: design (solution conceptual design, engineering design & system integration design), control system design, procurement/making parts, assembly and installation & commissioning.
Eight years exemption (without cap) are offered for the manufacture of automation machinery / automation equipment with engineering design including automation system integration design and control system design), while eight years exemption are given for the manufacture of automation machinery/automation equipment with engineering design including control system design), and five years exemption for assemble of robots or automation equipment or parts.
Mr. Chanin believed that the cooperation between the public and private sectors in encouraging the demand for and increasing the supply of robotics and automation systems will increase the overall productivity of Thai industry. More importantly, he is optimistic that the country will reduce its imports of industrial robots and automation systems.
Thailand has established a strong supply chain in the automation and robotics industries. A majority of firms in the industries are in the business of System Integration (SI) and mechanical brain & software development. This represents massive opportunities for foreign companies to investment in parts & components manufacturing.
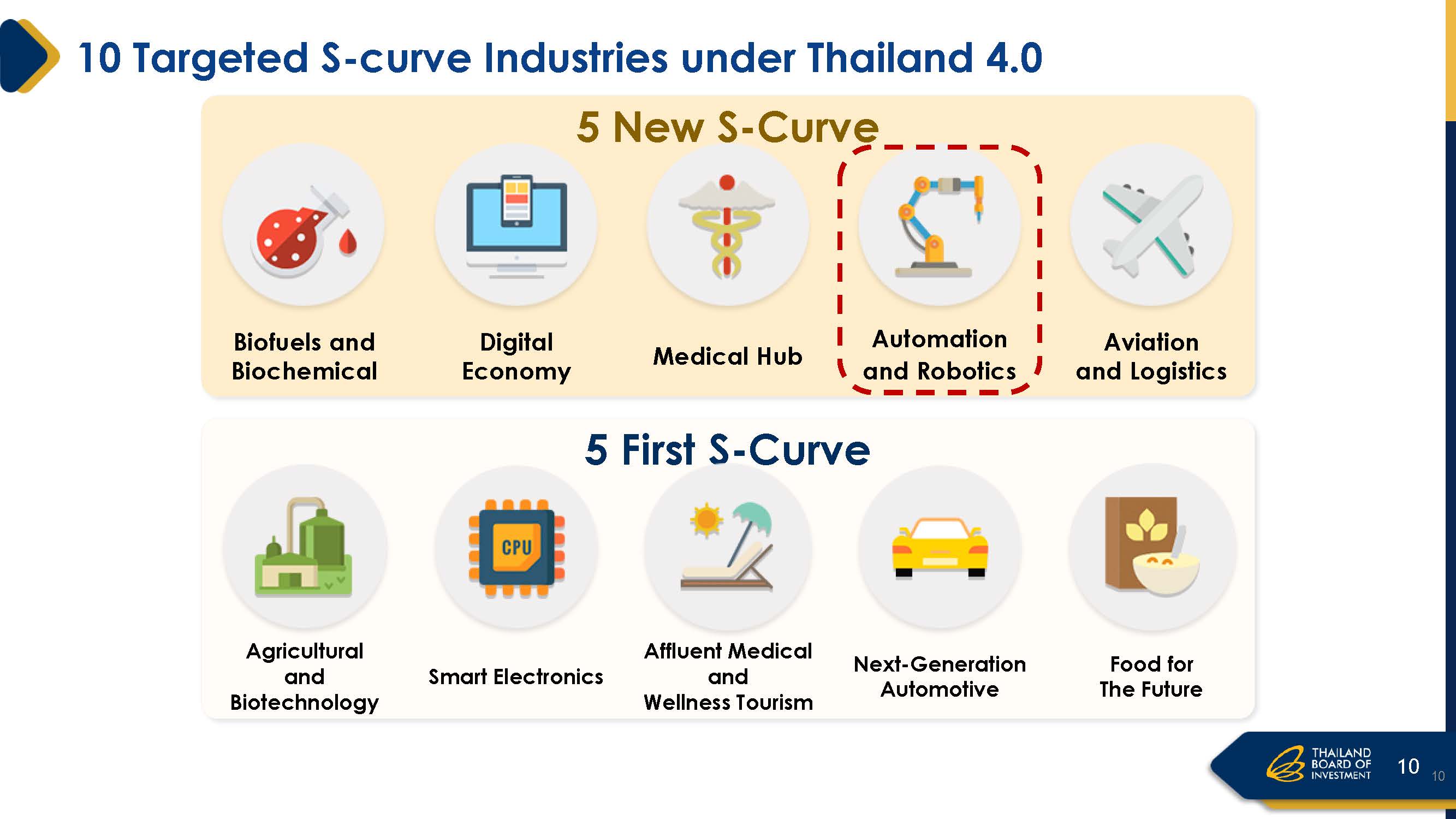
10 targeted S curve industries under Thailand 4.0
As Thailand is making big investments in automation and robotics, Mr. Chanin revealed that Thailand 4.0 aims to reduce inequality in the country by promoting modern, tech-driven solutions to enable access to public services even from the most remote parts of the country.
The Thailand 4.0 policy has highlighted opportunities and investment trends in 10 targeted industries, divided into two broad categories:
First 5 S-Curve industries include: agricultural and biotechnology, smart electronics, affluent medical and wellness tourism, next generation automotive and food for the future. This aims to enhance the competitiveness of the country current strengths through technology innovation.
The 5 New S-Curve industries are: biofuels and biochemical, digital economy, medical hub, automation and robotics, and aviation and logistics. This targets to develop five additional industries to accelerate on the new industrial base growth.
All of these industries stand to benefit from automation and robotics, ranging from improvements to major leaps in productivity.
Robotics and automation in the post COVID-19 era
In his speech, Mr. Chanin mentioned that due to the impact of COVID-19, the robotics market size is expected to increase significantly, from US$44.6 billion in 2020 to US$ 73 billion in 2025.
The demand for robotics and automation in the industrial and manufacturing industries is on a rise as well. The lower operating costs through automation and increasing productivity are driving the demand for robots and automation systems within the country.
Over the past few years, manufacturers are investing heavily in machinery and systems to stay competitive in the global digitalised manufacturing landscape and to meet the growing export demand in automobile and petrochemicals. About 50% of manufacturers in Thailand are considering adopting automation systems within the next 1-3 years.
He cited the driving factors of factors of robotics and automation adoption, which includes increasing production output rates, improving quality and consistency, increasing flexibility in product manufacturing, improving quality of working conditions, reducing material waste and increasing yield, saving space, reducing costs, and creating jobs.
Supporting factors
Thailand is considered an important growth market for automation and robotics here in South East Asia. With this in line, Mr. Chanin stated the institutions that provide support for research and development and human resource training. He also stated that some universities also offer specific programs, which mainly focus on robotics and automation engineering.
Thailand has a large supply of highly-skilled labour. On average, over 20% of all graduates each year study in automation and robotics related fields. In 2017, there were 346,100 new graduates from 148 surveyed universities and vocational schools. In that year, Thailand had 74,429 graduates in automation and robotics related fields, including 40,477 engineering students and 33,952 students in sciences, math and computing fields. The quality of Thailand’s students and graduates is internationally competitive. This is reflected in Thailand’s achievements in robot competitions and related events at the international and global levels.
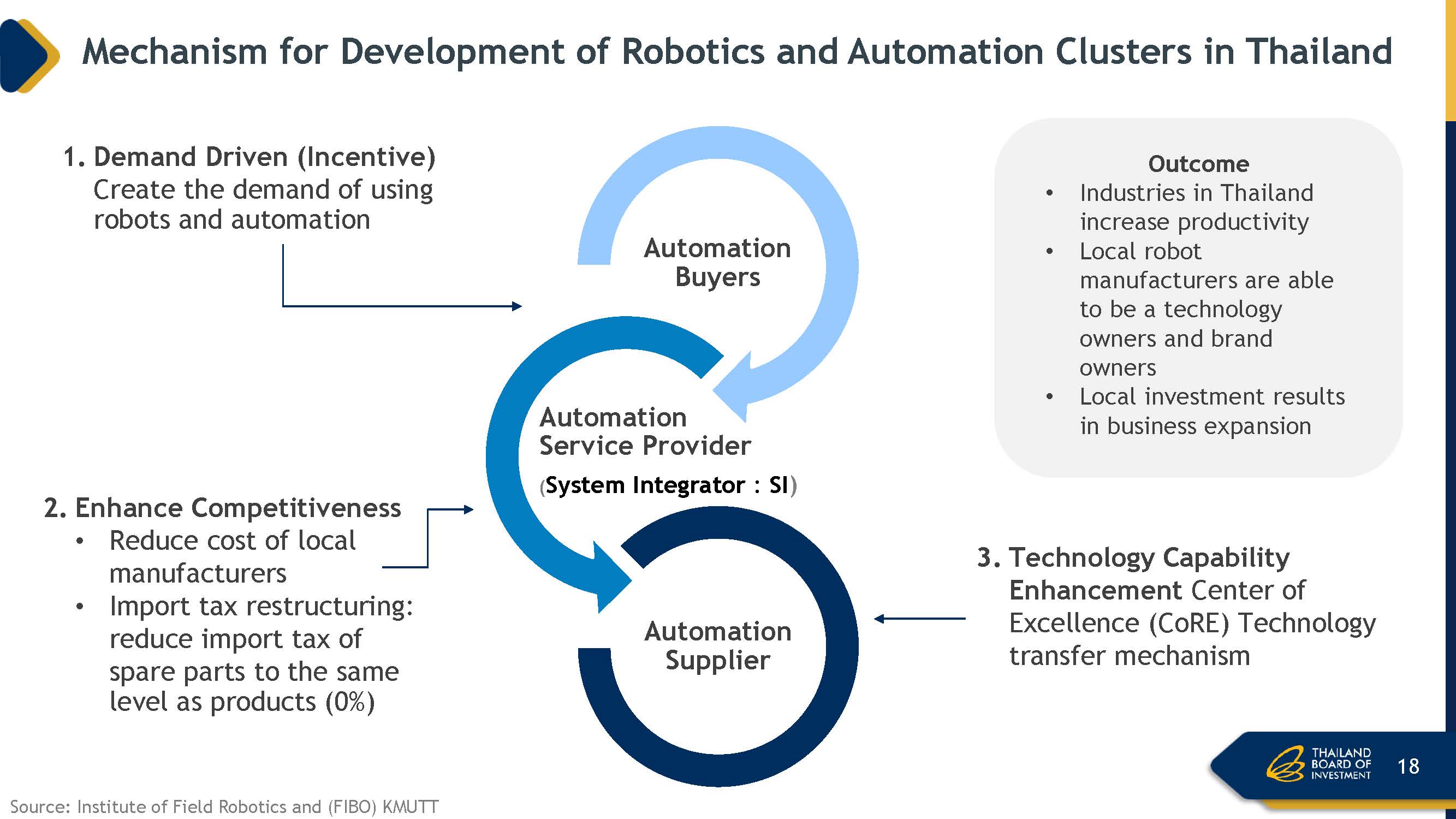
Mechanism for development of robotics and automation clusters in Thailand
1) Demand Driven (Incentive): Create the demand of using robots and automation
2) Enhance Competitiveness: Reduce cost of local manufacturers; Import tax restructuring:
reduce import tax of spare parts to the same level as products (0%).
3) Technology Capability Enhancement: Center of Excellence (CoRE) Technology transfer mechanism.
Industries in Thailand increase productivity. Local robot manufacturers are able to be a technology owners and brand owners, while local investment results in business expansion.
As is the case with many countries, Thailand is shifting towards an aging society. It can therefore be expected that there will be a decrease in the size of its workforce. This will create a need for enterprises to adopt robot and automation technology to compensate for the missing workforce. By 2030, it is forecast that 15% of Thai manufacturing workers will be replaced by robots.