PIGGYBACKING on the rising adoption of additive manufacturing in dental technology, companies specializing in 3D printing are offering new technologies to cater to digital dental laboratories.
Dental laboratories with additive production facilities act as service providers for conventional dental laboratories and dentists, using laser melting with metals for the industrial production of custom-fit and inexpensive dentures. This "digital" business model expands options in geometrical freedom, speed, pricing, and volume throughput unlike conventional manual milling and casting techniques.
Creating value
Concept Laser’s Mlab cusing and multilaser technologies target digital dental applications.
Oliver Edelmann, global sales & marketing vice president, said that although digital dental technologies is just a small part of Concept Laser’s business, the specific requirements of digital dental laboratories is an exciting segment. “Although dental technology is not the greatest mainstay of turnover, it is a technically very sophisticated segment that is continuously growing and also has extensive potential worldwide,” he said.
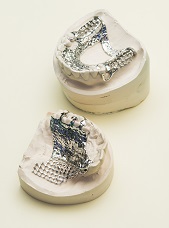
 Dental laboratories can convert to digital production and tap new potentials for the creation of value with the Mlab cusing R (Photo © Concept Laser GmbH)
Dental laboratories can convert to digital production and tap new potentials for the creation of value with the Mlab cusing R (Photo © Concept Laser GmbH)
An important model for dental technology, the “small” patented drawer principle allows material to be changed quickly without the risk of contaminating powder materials. The user-friendly pull-out drawer system includes the build chamber with dosing chamber and the storage container.
“The entry-level model with small build spaces in XS format is a good opportunity for newcomers to adapt their dental skills to ‘digital applications and tap new potentials for the creation of value,” Mr. Edelmann said,
Of particular interest to dental technology is the 200 W laser as it makes very sophisticated components possible, rendering it ideal for multi-unit bridge structures. It yields extremely high surface quality.
“A new feature is the multilaser technology with 2 x 200 W lasers, which can, of course, also process reactive materials, such as titanium,” Mr. Edelmann explained.
Solutions adopting multilaser technology can enable digital service centers to venture into industrial mass production. With its 2 x 200W lasers, the M2 cusing multilaser can produce 80% to 100% more components within the same time frame than the M2 cusing with 1 x 200W laser. The increase depends on the geometry of the corresponding component.
The new M2 cusing features a modular and fully integrated design that is both user and service friendly. This closed solution is suitable for limited space requirements while providing dental laboratories greater access to system components.
The product incorporates a completely new filter concept with a bigger filter surface of 20 m² compared with the previous 4 m². Designed with fixed tubing, the new filter module is completely integrated in the system, which reduces the changeover interval of the filter and increases overall system availability. This is even more noticeable with the use of multilaser technology with the accompanying increase in smoke particles.
“Significantly faster build rates require reliable filter change concepts. Every filter change has to be quick and easy. We have developed the new filter technology particularly under safety-relevant aspects based on the ATEX directive,” Mr. Edelmann said.
To ensure safety during filter changes, the M2 cusing comes standard with a filter that can be immersed in water and can be changed without touching a reactive filter cartridge. In line with the company’s emphasis on convenience and safety, the component is in an encapsulated glove box system, removed outside the process chamber.
Digitization of dentures
Renishaw, the UK's only manufacturer of metal additive manufacturing (3D printing) machines, is now supplying its AM250 metal 3D printing machine fully optimised for producing dental parts, meaning that it will not require further adjustment to achieve the production of high quality frameworks. To further enhance this offering Renishaw will also supply cobalt chrome powder that can be used in the manufacture of dental frameworks.
 3D printed RPD, polished and ready for build up (Photo © Renishaw)
3D printed RPD, polished and ready for build up (Photo © Renishaw)
While many digital removable partial dentures (RPDs) would be printed in wax and then invested and cast, Renishaw's AM250 additive manufacturing machines allow this step to be bypassed and manufacture directly in a dental grade, CE-marked cobalt chrome (CoCr). In the process’ most simplistic form a thin layer of metal powder, 20 microns thick, is consolidated with a super fine laser beam and the dental framework is built up layer-by-layer. It is extremely good at producing highly detailed complex surfaces. Virtually all the features that are in the design can be replicated without any loss of detail.
These exciting new developments have only been made possible due to Renishaw's extensive experience of 3D printing dental frameworks, which has been gained by supplying hundreds of thousands of high quality dental devices and frameworks to European dental laboratories.
Suitable for 3D printing of a large variety of metal dental devices, the optimised AM250 is a high volume 3D printing machine specifically aimed at the dental market. Fine tuned to the intricacies and challenges of dental devices, it is a popular alternative for those aiming to reduce the costs associated with milling operations and can replace traditional wax casting techniques by building dental frameworks from STL data as part of a digital workflow. Renishaw has conducted its development with an emphasis on accuracy and quality of frameworks, quality and traceability of raw materials, and speed and reliability of manufacture. The key aim is to allow a rapid return on investment for its customers.
As with any large scale manufacturing equipment, 3D printing machines would typically require further process development before they meet a company's quality criteria. In addition there can be further operational and intellectual property issues that may need to be addressed. Renishaw limits the need to carry out such activities by optimising the AM250 to produce dental devices to the requirements of its customers, meaning that they are able to produce production quality frameworks from the moment their machine is signed over. Renishaw can also offer assistance on all peripheral items such as IP licences, materials and part handling.
Renishaw also supplies the unique Renishaw Dental Studio (RDS) CAD package that combines the speed and flexibility of the company's DS30 blue light scanners with the accuracy of the Renishaw DS10 contact scanner. Using Exocad, RDS allows a wide range of dental devices to be designed. The ability to add to the software's capability through additional modules makes the package flexible and scalable for the expanding dental laboratory.
Certified materials
The certification and validation of materials for additive dentures are of great significance to the dental sector. Aside from certified CoCr, biocompatible materials such as titanium and palladium can be used on a Concept Laser Mlab cusing R or M2 cusing.
Titanium is suited ideally for the combination of high rigidity and strength, e.g. for thin removable partial dentures, parts with thin cross sections or braces, but is also an ideal dental material for allergy sufferers. The biological benefits are utilized in combination with laser melting and ceramic veneering. The LaserCUSING process on a Concept Laser Mlab cusing R or M2 cusing allows the economical production of caps, bridge structures, cast parts, primary and secondary structures, as well as implant supra-constructions made of the rematitan CL, a pulverized titanium alloy from Dentaurum.
PAL KERAMIT 3-S, a palladium-based dental fire-bonded alloy from Nobil Metal, is bio-compatible and certified. The Italian company has been operating in the area of powder metallurgy for the dental sector for a long time and therefore has a wealth of experience in this area.
The composition of PAL KERAMIT 3-S is distinguished by good compatibility with conventional veneering ceramics, a light oxide and low specific density, resulting in good value for money.The palladium alloy easy to process and is also suitable for complex structures, such as implant bridges. The entire powder production process is certified according to EN ISO 9001-13485.
Nike Air Jordan 1 Mens
 iConnectHub
iConnectHub
 Login/Register
Login/Register Supplier Login
Supplier Login



























