
By: Kathryn Gerardino-Elagio
The manufacturing industry is in the midst of a profound evolution as it navigates the challenges and opportunities brought about by the post-pandemic landscape. Several pivotal trends are poised to define the trajectory of manufacturing in 2024, encompassing digital transformation, sustainability initiatives, bolstering supply chain resilience, and fostering collaboration between humans and AI. These trends will empower manufacturers to elevate their operational efficiency, elevate product quality, drive innovation, and fortify their competitive edge in the global market.
In a recent discussion, International Metalworking News for Asia (IMNA) asked Simon Ng, Partner Sales Director, Strategic Engagement, Asia Pacific South at Dassault Systèmes, delving into the impact of these trends on the manufacturing sector. Ng also provided valuable insights into strategies that manufacturers can adopt to not only survive but thrive in the ever-evolving landscape of 2024 and beyond.
IMNA: What are the primary factors and obstacles influencing the industrial manufacturing sector in Southeast Asia?
Simon Ng: Southeast Asia’s main economic business drivers in 2024 amidst global uncertainties will be dependent on the following;
A. Rising labour cost in China, coupled with continuous trade and political tensions. This is projected to result in the shift of manufacturing from China to various Southeast Asian nations in the long term.
B. Many countries in Southeast Asia i.e. Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam are extensions of the high tech and electronics industry ecosystem that will continue to boost the region’s growth in industrial manufacturing.
C. Other factors driving growth for industrial manufacturing in Southeast Asia are energy-related, construction industry boom in countries like Indonesia and Philippines. Expansion of Electric Vehicle (EV) supply chain in Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, Vietnam and Malaysia.
D. The region is also home to a population of more than 600M and with a combined GDP of over US$4 trillion, forms the largest economic bloc after USA, China, Japan and EU.
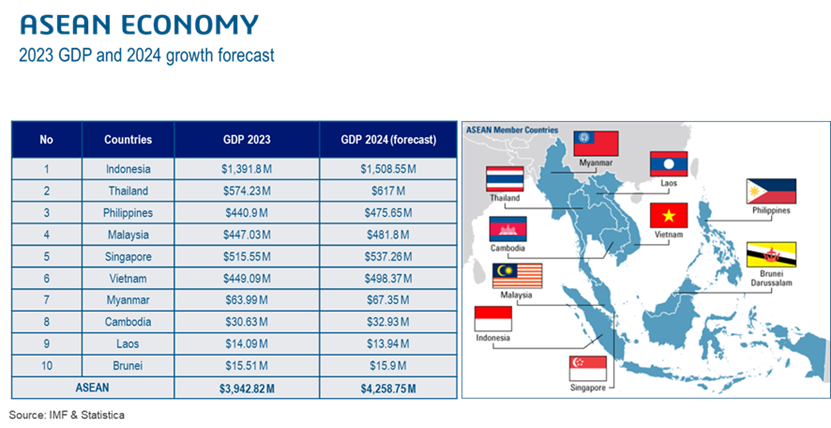
The challenges that economies face in Southeast Asia includes:
E. Uncertainty in global economies, downward pressure on demand from advanced economies where Southeast Asian nations typically export to. This has a direct impact on manufacturing activities.
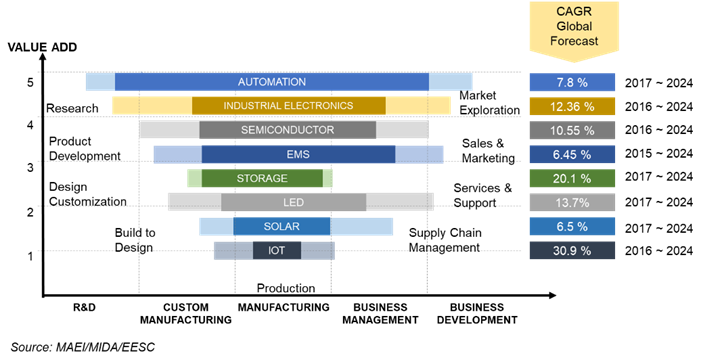
F. Southeast Asian nations are well-known to be contract manufacturing bases. Classified as middle income countries (with the exception of Singapore and Brunei), they are extensions of advanced economies and only form part of the ecosystem with lower labour cost, abundance of raw materials. As shown in the diagram below, the main activities that take place in these countries are related to ‘manufacturing’ or ‘production’ instead of the higher value added design or product development activities in the electronics industry.
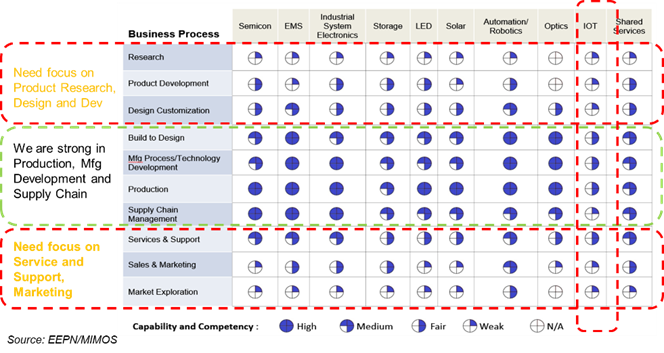
G. Southeast Asian economies are overly focused on low cost production of selected industry sub-segment’s electronics systems, as opposed to evolving into a knowledge based economy centred on research and development of advance industry segments such as IoT. The diagram below illustrates the region’s capabilities in selected industry segments and value added production activities.
IMNA: What are the most effective approaches and tactics for industrial manufacturing companies to address the challenges posed by the energy crisis, global competition, and evolving customer demands?
Simon Ng: Some of the best practices or strategies for Southeast Asian industrial manufacturing companies include:
H. To improve value proposition of contract manufacturers to become ODMs (Original Design Manufacturer) or even OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturer) in the future. Instead of investing in the bare minimum for production, Southeast Asian companies should adopt ‘Kaizen’ and continuously improve its existing processes towards best-in-class. Take on additional value added activities such as product substitution i.e. Japanese or Chinese manufacturing companies in the last decades.
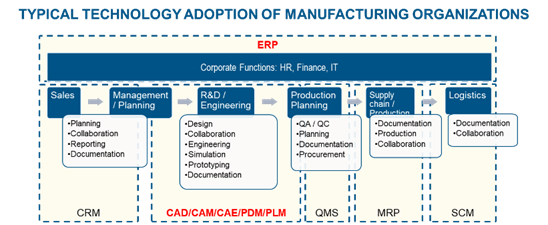
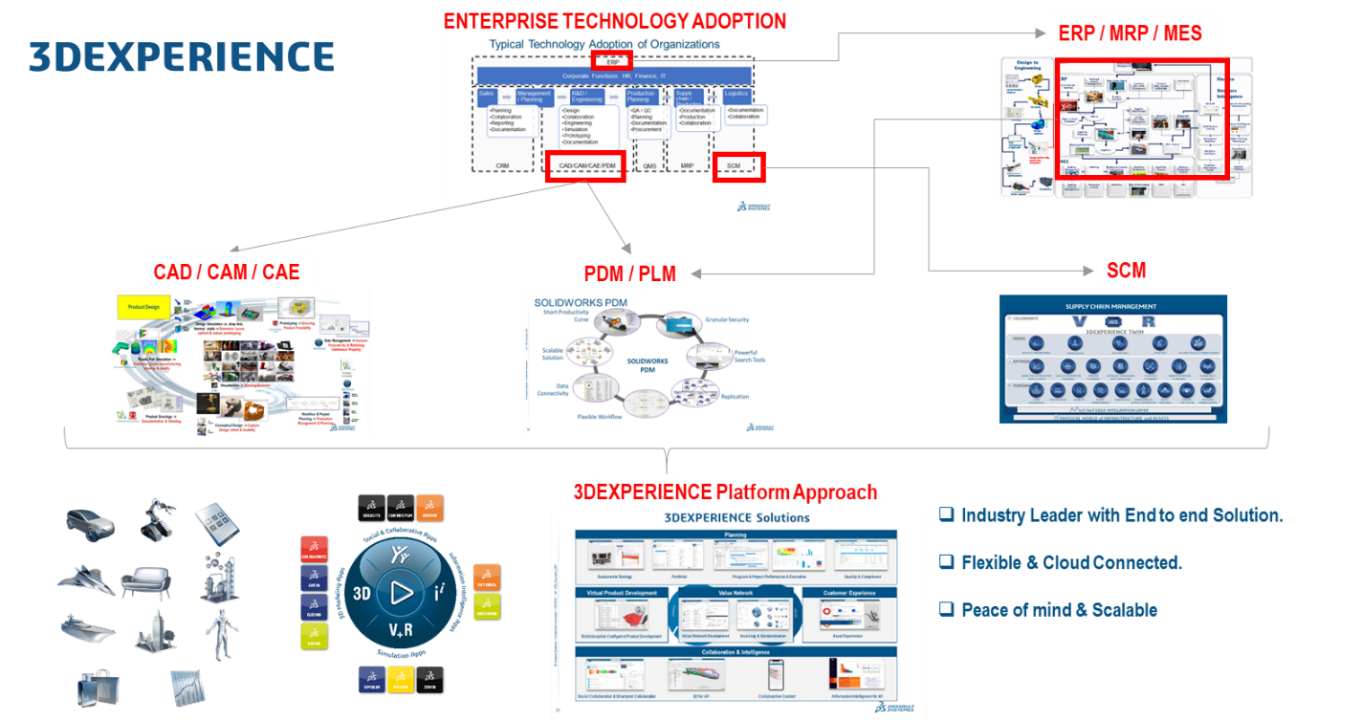
I. In order to do the above, Southeast Asian companies need to continue expansion towards higher value added activities of the entire industry value chain. E.g. adopt enterprise technology solutions, upskilling of workers, expand R&D capabilities. The diagram below depicts the typical technology adoption of manufacturing companies.
J. Adopt best-in-class enterprise solutions of the OEMs in Product Lifecycle Management, Enterprise Resource Planning, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL) and Generative AI in various application levels from ideation, validation, process automation, and reporting and customer interactions e.g. chatbots, big data for machine learning of customer behaviors, generative design to explore various options of design or weight saving/cost saving. The diagram below shows various industry segment requirements, their business models and business tiers.

IMNA: What will be the impact of generative AI and other emerging technologies on the industrial manufacturing industry in terms of innovation, productivity, and quality?
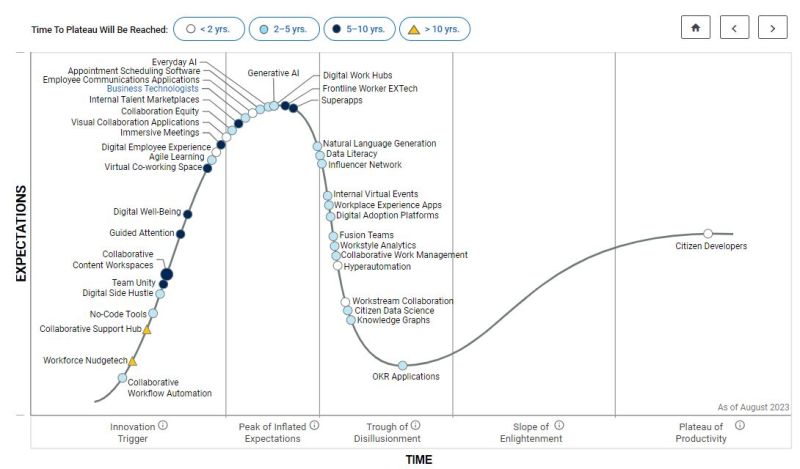
Simon Ng: AI, ML, DL and Generative AI technologies are continuously being researched and added to various cloud-based technologies in order to improve the entire product lifecycle process. Refer to the diagram below for a typical product lifecycle process and Gartner’s 2024 Hypercycle of emerging technologies with Generative AI at the peak of inflated expectations;
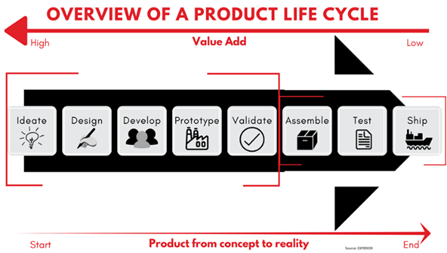
K. Ideation: Conceptual design to create, review and to evaluate before embarking on the entire design to manufacturing process with various technologies such as cloud, free form, generative design to determine function before form and etc.
L. Design: Utilizing 3D modeling approaches, from top down design to capture design intent, to generative design in order to reduce weight, explore design options and alternate manufacturing processes. E.g. latticing, alternate materials, additive manufacturing and etc.
Modeling Simulation (MODSIM) concepts for early insights of product performances and to reduce prototyping with the use of machine learning and various mathematical models. E.g. finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and etc…
M. Development: Explore Virtual Twin concepts, improve production and simulate system commissioning in order to optimize processes.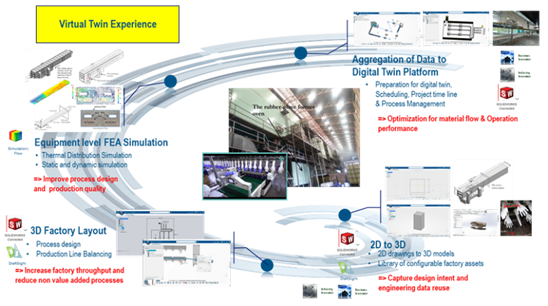
- N. Prototyping: Use of various machine learning and deep learning technologies for fabrication process, from additive manufacturing technologies with 3D printing and further improve subtractive manufacturing technology of generating high-speed or smarter toolpaths for various Computerized Numerical Control machines processes.
- O. Validation: Generative AI technology to assist in making various product and manufacturing decisions. E.g. front–end loading concepts for the execution of details engineering, procurement and construction for accurate project costing.
- P. Assembly: Use of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Technology for sales configurators to expand sales online or in global dealerships and improve assembly instructions in the shop floor to improve cycle time.
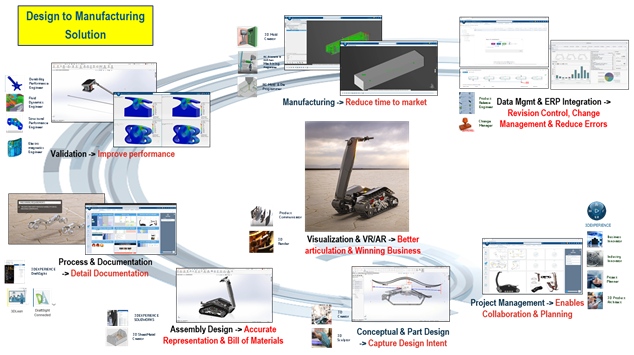
- Q. Test: Utilization of AI in total quality control (TQC) processes; for measurement, validation, documentation and reporting to the connected enterprise system for product lifecycle and release management.
- R. Shipping: Complete logistics applications of connected enterprise resource planning and supply chain management solution to ensure seamless process integration and customer experience.
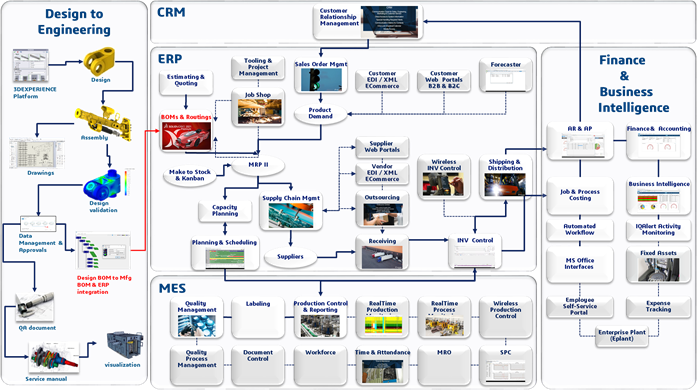
Dassault Systemes’ thought leadership concept known as 3DEXPERIENCE is a unified platform of all processes filled with leading edge AI technology from ideation, validation, production to logistic solutions for various industry applications with best-in-class tools to lead industrial manufacturing companies in southeast asia to overcome challenges, encourage innovation, increase productiviy and improve quality.




 iConnectHub
iConnectHub
 Login/Register
Login/Register Supplier Login
Supplier Login


























