Polymers and plastic products dominate the modern healthcare sector. From tubes to MRI machines, plastics not only make healthcare simpler but far less painful.
The most innovative of medical procedures today have become increasingly dependent on plastics. Re-usable and antimicrobial plastics are helping medical experts overcome challenges as these offer advantages that aid in the performance of medical procedures and efficient drug delivery.
In this area, antimicrobial plastics have become popular as they lead to fewer infections by repelling or killing bacteria when surfaces aren’t cleaned regularly. Though new, this technology has the potential of helping patients stay healthy longer. For a very long time, antimicrobial additives have been used in a number of medical devices. Some antimicrobials are designed to release from the surface to react with pathogens and the antimicrobial disables the microbe to multiply into colonies. The only limitation of such antimicrobials is its duration.
Additional use of antimicrobials should be avoided though due to its cost and also to avoid development of super-strains of new bacteria. It would damage a product and its surrounding after its shelf life has ended. Drug-resistant bacteria and strains are often linked to the over-consumption of antibiotic medicines. Also once the plastic devices are thrown, they end up in landfills where there is the impending fear of antimicrobials leaching from the plastic and polluting the environment.
A report from MarketsandMarkets projects the global antimicrobial plastic market to reach $3.6 billion by 2020 registering CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 10 percent between 2015 and 2020. The packaging and healthcare segments are the two major applications of the antimicrobial plastic market with major market share in 2014, and is projected to dominate the global market by 2020 mainly due to the growth of innovative ways to proactively inhibit microbial growth on surfaces of plastic products and medical equipment.
3D printing in the medical field
3D printing in medical application is a hugely growing market as the demand for speedy medical solutions increases. Research and development facilities in companies are supporting the demand for 3D printing in medical applications. Also medical manufacturers are under pressure to develop cost-effective, innovative products and 3D printing is being used increasingly.
A report Global Industry Insight: 3D Printing in medical applications issued by P&S Market Research suggests that North America will be leading the global 3D printing market in medical applications in the coming years due to technological advancements to grow the scope of medical applications. Europe is the fastest growing region in the global 3D printing in medical applications market. The major reason for the fastest growth in the region is increasing government funding in 3D printing market. The report identifies some of the companies operating in 3D printing in medical applications market are Eos GmbH Electro Optical Systems, Materialise NV, EnvisionTEC GmbH, 3D Systems Corporation, Nanoscribe GmbH, Voxeljet Technology GmbH, and Stratasys Ltd.
The medical industry is using 3D printing in multiple ways. Robohand® is using Makerbots® to create prosthetics that are cheaper than traditional ones while technicians can now also print exact 3D reproductions of specific body parts using scan from MRI machines. 3D printing is an additive technology where parts are build layer by layer to create an operational, functional element. Advances in 3D printing technology have enabled parts created with materials such as plastic resins to metals.
Prosthetics is one of the biggest medical areas benefited from 3D printing technology. Surgical training and procedures have been greatly benefitted by 3D printing. In Japan, 3D replicas of cancerous kidneys have been made while in USA; doctors have started printing ribcages to treat potential congenital defects in babies.
3D printing is also a viable technology for instrument creation including surgical tools and life-saving devices. With additive manufacturing, it is cheaper to produce tools which can be created as needed.
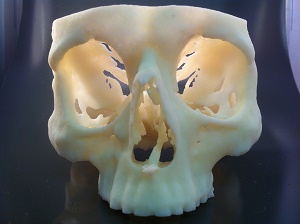
Cranium produced on a Stratasys Objet30 Pro 3D Printer
New materials demanded
SABIC Innovative Plastics continues to offer new materials and processing expertise to support customers in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industry. The company via its recent innovations addresses important trends such as enhanced processing, greater compatibility with blood and proteins, greater environmental safety, etc. SABIC with its new CYCOLOY™ HCX1640 resin can enable manufacturers to design robust, light and attractive drug delivery devices such as insulin pens that meet standard healthcare regulations.
Cathie Hess, Director of Healthcare Marketing for SABIC’s Innovative Plastics business was cited as saying: “Our new material helps manufacturers achieve thin walls and dimensional stability, as well as improved weld line performance and impact resistance, meaning that the devices are safer and less likely to break. These features also allow manufacturers to create complex designs that are capable of integrating an increased number of mechanical or electronic features. Additionally, the resin has a wide range of color options, helping to create an attractive design that appeals to patients.”

SABIC’s CYCOLOY™ HCX1640 for light drug delivery devices such as insulin pens.
SABIC’s broad and diverse polymer range and engineering thermoplastics solutions has helped customers meet medical challenges. From polymer based materials such as SABIC® PP PCGR40 and SABIC® PP PCGR40L offering accuracy, efficiency and precision in drugs delivery to engineering thermoplastic technologies such as SABIC’s ULTEM™ resins and LNP™ antimicrobial compounds, SABIC is committed to working with medical device manufacturers to find solutions offering improving healthcare trends.
DuPont™ Hytrel® thermoplastic polyester elastomer, Delrin® acetal resin and glass-reinforced Zytel® nylon are being employed for use in NuDrive, the world’s first lightweight and compact lever-drive accessory for manual wheelchairs. It reduces the force and thrust required to self-propel a wheelchair by up to 40 percent offering cost-effective and lighter options than metal components. Disposable and reusable insulin pens are manufactured using several DuPont grades such as Crastin®, Hytrel®, Delrin®, and Zytel® polymer families. These resins are deployed in ratchets and gears which function as the delivery system of such pens.
DuPont also offers materials that can withstand any conditions for every possible sterilisation approach while its plastics also offer low wear/low friction applications both in self-contact and with other materials such as steel. DuPont is also offering its DuPont™ 20 Series Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) to package brands of unit dose inhalation drugs. Diane Hahm, DuPont technical consultant was quoted as saying: “The pharmaceutical industry is very resistant to change due to regulations. One of the best things about the DuPont™ 20 Series LDPE resin is that it is the same as it was when it was initially used back in 1973. It was the first resin used in the B-F-S process and continues to be the premier choice today for quality and reliability of supply.”

 iConnectHub
iConnectHub
 Login/Register
Login/Register Supplier Login
Supplier Login



























